近日,2019级浩青班邝宇航同学及团队成员在省级大学生创新项目的资助下,利用基质调整实现了Eu2+激活荧光粉热稳定性从反热猝灭到零热猝灭的调控。成果发表在Journal of Materials Chemistry C上。
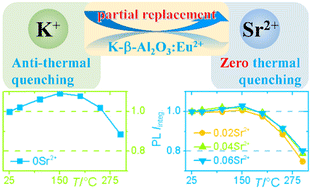
High quantum efficiency and high thermal stability have always been two indicators to measure whether phosphors have excellent luminescence performance. In this paper, a series of blue-emitting K-beta-alumina phosphors K0.90−xSrxAl11O17+d:0.2Eu2+ were successfully synthesized by introducing Sr2+ to partially replace K+ ions. The internal and external quantum efficiencies can be improved to 92.4 and 73.4%, respectively, for x = 0.06 with the introduction of Sr2+. More importantly, the anti-thermal quenching properties of the original phosphor (without Sr2+) can be successfully regulated to zero thermal quenching within 150 °C by partially replacing K+ with Sr2+. Thermoluminescence spectra suggest that the introduction of Sr2+ reduces the content of shallow traps related to VO and increases the deep traps related to VK. The introduction of Sr2+ is accompanied by the decrease of the (K,Sr,Eu)/Al ratio, which leads to the weakening of structural rigidity. As a result, the dynamic equilibrium between the non-radiative process and the anti-thermal quenching process facilitates the zero thermal quenching. A phosphor-converted light-emitting diode (pc-LED) with a high color rendering index (CRI = 91.6) and low correlated color temperature (CCT = 5108 K) also shows the great potential of this phosphor in white pc-LEDs.
第一作者:邝宇航(已保送至华南理工大学)
通讯作者:张吉林
发表期刊:Journal of Materials Chemistry C(IF 8.067)
在线发表时间:2023-04-07
文章链接:https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2023/TC/D3TC00698K
