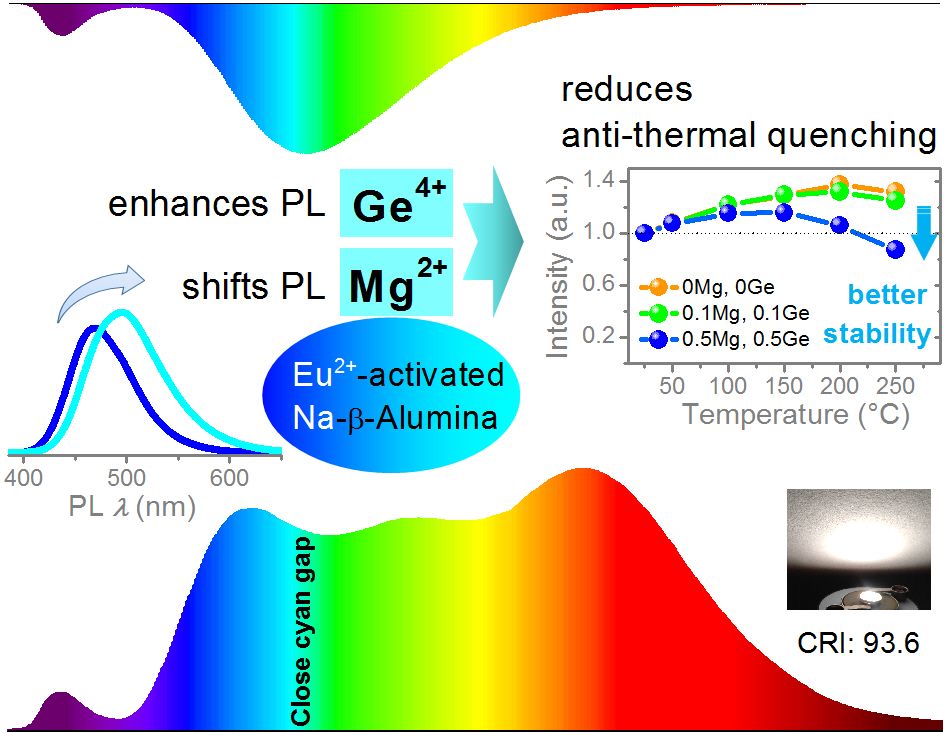
Broadband cyan-emitting phosphors are crucial to close the cyan gap of phosphor-converted white light-emitting diodes (pc-WLEDs) for full-spectrum illumination. In this work, efficient cyan-emitting Eu2+-activated phosphor is achieved through structural modulation, which exhibits anti-thermal quenching behavior. Redshift from blue (469 nm) to cyan (500 nm) emission and enhancement of emission is achieved by codoping Mg2+ and Ge4+ into Eu2+-activated Na-beta-alumina phosphor. The introduction of Mg2+ ions dominates the redshift, while Ge4+ dominates the enhancement of emission. Furthermore, the introduction of Mg2+ and Ge4+ reduces the content of deep trap levels related to VNa defect, which decreases the degree of anti-thermal quenching and results in better thermal stability. The prototype pc-WLED by using the cyan-emitting phosphor exhibits higher color-rendering index and potential to close the cyan gap of pc-WLEDs for full-spectrum illumination. This work presents a paradigm for exploring phosphors with highly efficient and thermally stable emissions.
第一作者:陈梦芳
通讯作者:廉世勋,张吉林
发表期刊:Advanced Materials Technologies
发表时间:2023-10-02
文章链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/admt.202301170
