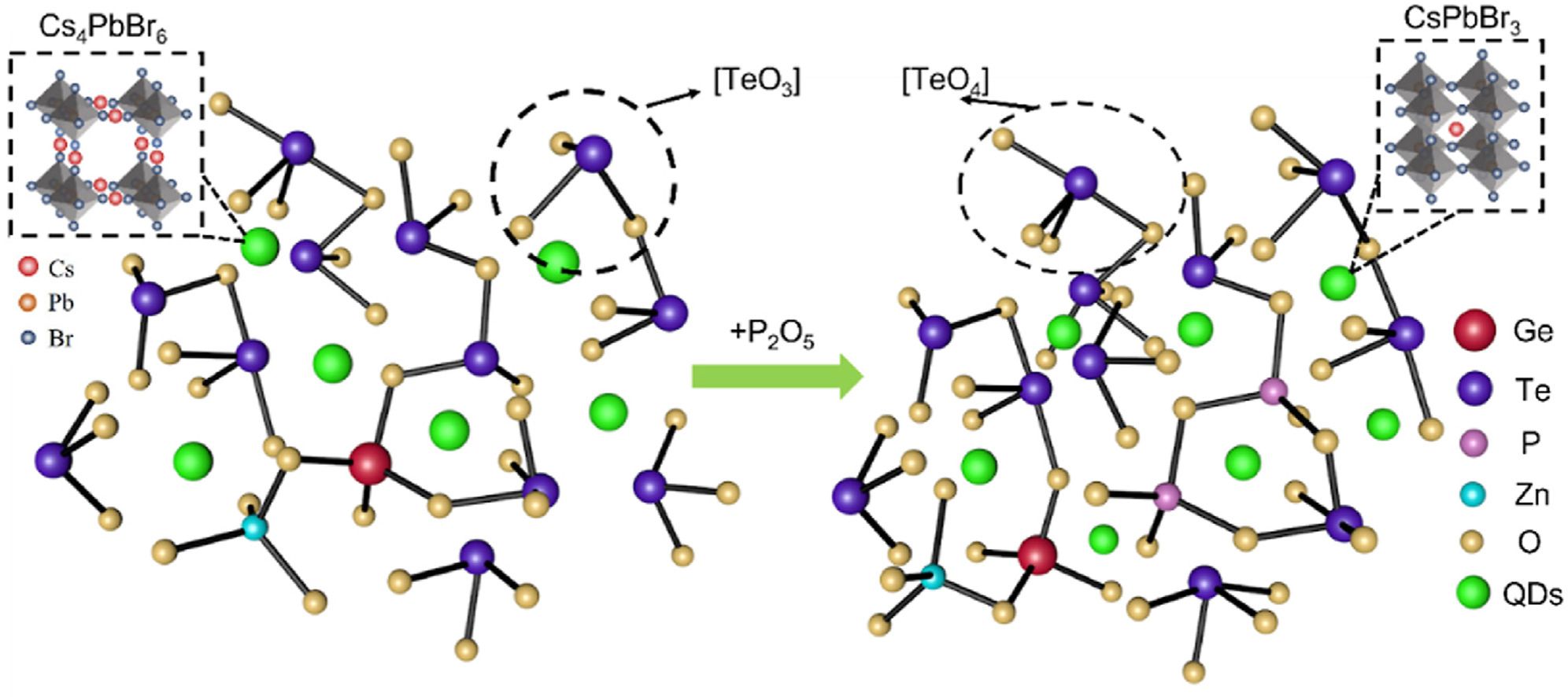
All inorganic perovskite quantum dots (QDs) have broad applications due to its unique photoelectric properties. At present, a large number of QDs embed glasses of three-dimensional (3-D) CsPbBr3 cubic phase or zero dimensional (0-D) Cs4PbBr6 hexagonal phase have been reported, but the phase regulation between 0-D and 3-D has not been deeply studied only by the adjustment of the glass network topology. In this paper, Cs4PbBr6/CsPbBr3 QDs were successfully synthesized in tellurite germanate glass by high-temperature melt-quenching combined with in-situ crystallization, and their luminescence properties, structures, and phase regulation fundamentals in glasses were investigated in depth. The introduction of P2O5 increases the ratio of [TeO4]/[TeO3] units in the tellurite germanate glasses, resulting in a more compact glass network and changing the growth environment of QDs. When the content of the nucleating agent P2O5 was increased to 3% (mass fraction), the crystalline phase of QDs realized the regulate from 0-D hexagonal phase to 3-D cubic phase. The regulation from Cs4PbBr6 to CsPbBr3 is accompanied by a blue-shifted emission peak from 519 to 482 nm, and the synthesized QDs glasses all have good long-term stability. The QDs glasses obtained in the experiment has great potential in the application of white light emitting diodes.
第一作者:赵晓,沈帅龙
通讯作者:余丽萍
发表期刊:Journal of Luminescence
在线发表时间:2023-05-16
文章链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022231323002429
